Agricultural Districts provide protection for farm operations; 203,000 acres in Genesee County are enrolled
New York State Agricultural Districts, especially in counties such as Genesee where farming is vital to the local economy, are significant geographic regions that enable farmers to work with their municipalities to best serve their communities.
That was a key point of a recent webinar conducted by Jeff Kehoe and Kathleen Tylutki, farmland protection specialists with the NYS Department of Agriculture and Markets, Division of Land and Water Resources, Agricultural Protection Unit.
Agricultural Districts are defined as locally initiated mechanisms for the protection and enhancement of agricultural land as a viable segment of the local and state economies.
“Back in 1971-72, the ag district program was developed to help stem the tide of suburbanization moving into the countryside,” Kehoe said. “It’s really not a matter of the farmer and the department; there’s a lot more to this. In New York State, towns have local authority and they have the ability to control what happens in their town and jurisdiction.”
In 2020, there were 165 Agricultural Districts in 53 counties in New York, consisting of 26,227 farms and accounting for 9,149,836 acres.
“It’s a very successful program and each year we have been growing,” Kehoe reported. “And in light of recent events, hopefully we will see more and more properties enroll in the ag district to better accommodate agriculture and allow farmers to scale up their operations without too much scrutiny from the town.”
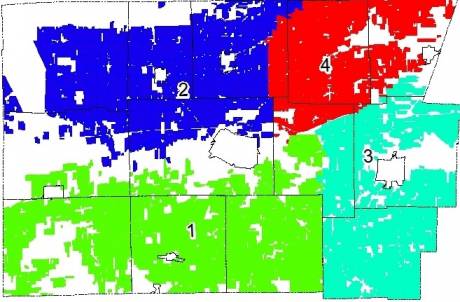
In Genesee County, according to Planning Director Felipe Oltramari, there are four ag districts, covering 6,200 parcels and 203,000 acres.
“The number of acres is about two-thirds of the total land area in the county,” Oltramari said.
The Genesee County districts are as follows (see map below):
District 1 (green) – Darien, Alexander, Bethany and a bit of Pembroke, Batavia and Stafford.
District 2 (blue) – Alabama, Oakfield, Elba and northern parts of Pembroke and Town of Batavia.
District 3 (aquamarine) – Le Roy, Pavilion and parts of Stafford and Bergen.
District 4 (red) – Bergen, Byron and small parts of Elba, Stafford and Le Roy.
Oltramari said enrollment into an ag district is free and voluntary, and that individual district reviews occur every eight years from the district’s creation date.
“This process is undertaken on behalf of the Genesee County Legislature by the County Department of Planning,” he said. “During review, landowners within the district boundaries may enroll or withdraw property from the district. Only entire parcels may be included or excluded.”
Kehoe said that “the power of this program is given to the counties because local (town, village) government has so much control over what happens in their towns.”
“If you are a farm operation – which is a technical definition in our law – and your parcel is enrolled in the agricultural district, the circumstances are that it’s modified,” he said. “Your local laws are modified if you’re a farm operation enrolled in an ag district.
“That still means that you must comply with all local laws and permits and applications and all the local processes, however, when you’re in the ag district, the town is essentially on notice to streamline or facilitate your applications, minimize any fees and, hopefully, work with you to be as timely as possible and least burdensome as possible.”
Agricultural Districts are overseen by a county’s Agriculture and Farmland Protection Board – an 11-member committee under the direction of the county legislature. It is tasked with advising the legislature in matters relating to establishment, modification, continuation, or termination of agricultural districts.
The AFPB also issues recommendations to the legislature in regards to the Agricultural District Annual Enrollment and Smart Growth Plan revisions.
“It’s a different level of government that has oversight and can weigh in on ag issues,” Kehoe said.
In Genesee County, current AFPB members are Donn Branton, chairperson, farmer; Janice Beglinger, Agriculture Outreach educator Cornell Cooperative Extension; Steven Boldt, farmer; Kevin Andrews, director Real Property Tax Services; Christian Yunker, County legislator.
Also, Marcia Hirsch, agribusiness; LuAnne McKenzie, farmer; Dennis Phelps, Soil & Water Conservation District chairperson; Janette Veazey-Post, farmer; Tim Welch, Soil & Water Conservation technician, and Oltramari.
The AFPB, per Agriculture and Markets Law 25AA 302(c), shall render expert advice to the county legislature relating to the viability of lands to be enrolled in the agricultural district, including advice as to the nature of farming and the relation of farming in such area to the county as a whole.
Oltramari said specific recommendations could pertain to the proper placement of fire hydrants and water lines to not adversely affect farm operations, and the periodic reviews of the district itself.
Kehoe said that Right To Farm Laws provide additional protection for farmers, and come in three forms:
- Agriculture Districts Law, Article 25AA, Section 308;
- County laws that enact public policy supportive of agriculture;
- Local laws that typically support agriculture and Article 25AA and, sometimes, utilize the services of an ag mediation panel and/or require a statement on building permits.
According to Section 308, The Commissioner of Agriculture and Markets is authorized to issue opinions regarding whether certain agricultural practices are sound. Any practice that is determined to be sound does not constitute a private nuisance when an action is brought. In a nuisance suit where a farming practice is determined to be sound, this section ensures that the plaintiff will incur any fees and other expenses related to the defense. This section protects farmers from paying costly legal fees to defend their operations against frivolous nuisance actions.
Section 305-A of the Agriculture Districts Law “protects farmers against local laws that unreasonably restrict farm operations located within an agricultural district,” Tylutki said.
This section of the law calls for coordination of local planning and land use decision-making with the agricultural districts program, and ensures that local zoning, comprehensive plans and land use plans will not unreasonably restrict or regulate farm operations within an agricultural district unless there is a threat to public health or safety.
Tylutki said the keys for valid objections to local law infringement are that the parcel is enrolled in an ag district, it is the site of a legitimate farm operation, and that the farmer has exhausted all local administrative remedies before appealing to the NYS Department of Agriculture and Markets.
“Apply for it (protection status), get the denial and then the Department (of Agriculture) has something to react to,” she said. “So, then we actually have a hard denial to say to the town what is being unreasonable in consulting with your county AFPB and other local resources.”
She noted that an ordinance may appear reasonable in an abstract, but it could be unreasonably restrictive or regulate a particular farmer. All referrals are evaluated on a case-by-case basis.
Tylutki also spoke about farm stands and similar retail activities on ag district operations.
The rule of thumb for these ventures is that at least 51 percent of the agricultural crops, livestock and livestock products sold, on an annual basis, must be from the farm’s own production. Furthermore, the activity must be used as part of the direct marketing strategy of the farm operation and the primary purpose of the activity must be to sell the farm’s products/services, not to serve as a recreational use of the land.
Oltramari said that a prime example is the retail store and Community Supported Agriculture business at Porter Farms in Elba.
“They just opened a retail store and they have had the CSA for quite some time,” he said, explaining that a CSA allows citizens to purchase a membership and receive a weekly bag of produce from the farm.
“In an ag district, the farm is permitted to do this through the right-to-farm protections,” Oltramari said. “This is the same as wind or solar being used to offset utility costs of the farm. It also protects farmers against nuisance liability as long as the farmer is following the New York State ag district guidelines.”
-------------
Additional resources on Agricultural Districts and related topics can be found at the following:
Agricultural Value Assessment Program, Department of Taxation and Finance
https://www.tax.ny.gov/research/property/assess/valuation/agindex.htm
Jeremy Kergel Jeremy.Kergel@tax.ny.gov
Building Standards and Codes, Department of State:
https://www.dos.ny.gov/DCEA/
Local Government Services, Department of State
https://www.dos.ny.gov/lg/
Farm Brewery/ Cidery/ Wineries etc. State Liquor Authority
https://sla.ny.gov/
Industrial Scale Solar Arrays: NYS Solar Guidebook
https://www.nyserda.ny.gov/All%20Programs/Programs/Clean%20Energy%20Siting/Solar%20Guidebook
Agricultural District Mapping Program, Cornell University IRIS (Institute for Resource Information Sciences)
https://iris.cals.cornell.edu/extension/agricultural-districts/
Diane Ayers dag10@cornell.edu
Publication: Planning for Agriculture
https://farmlandinfo.org/publications/planning-for-agriculture-in-new-york-a-toolkit-fortowns-and-counties
