Alexander highway superintendent looking for grants to deal with flooding of Tonawanda Creek
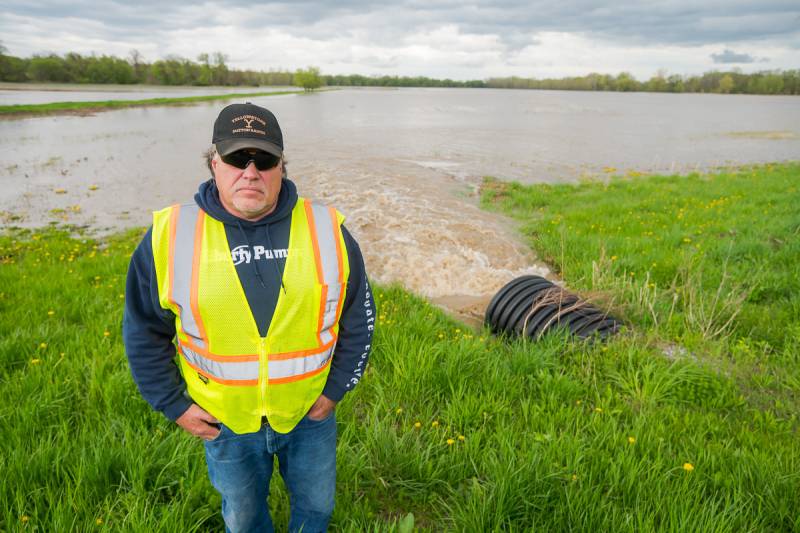

Photo by Howard Owens.
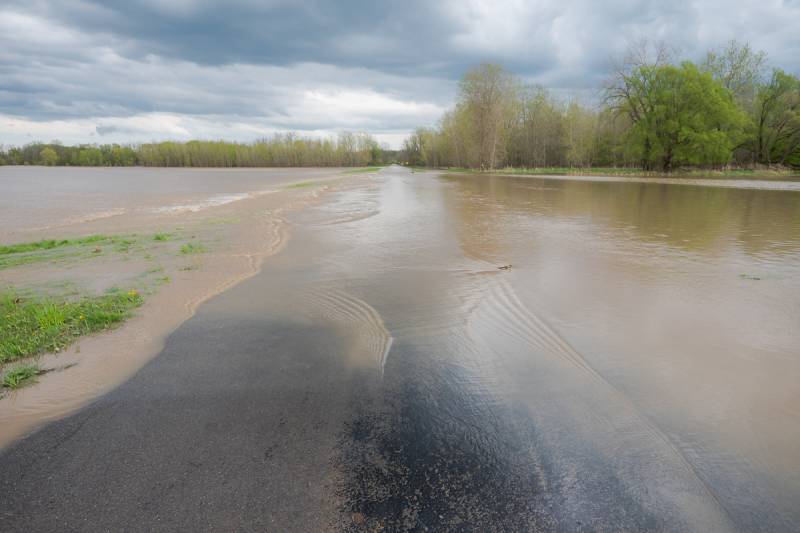
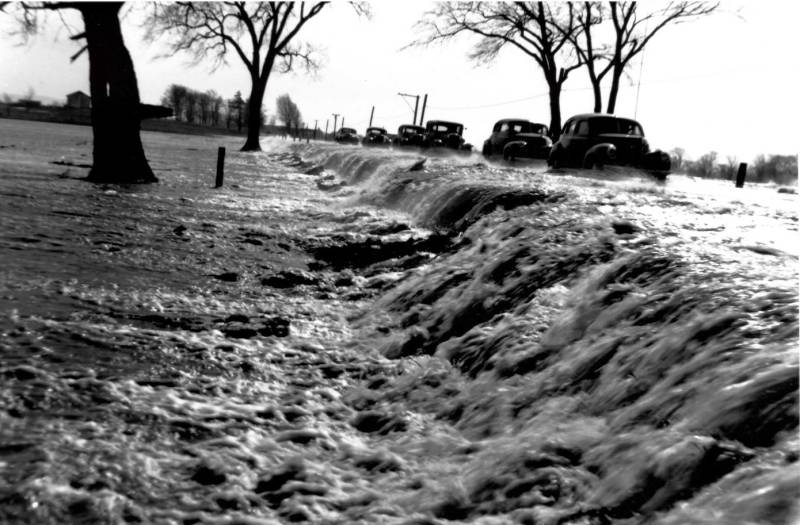
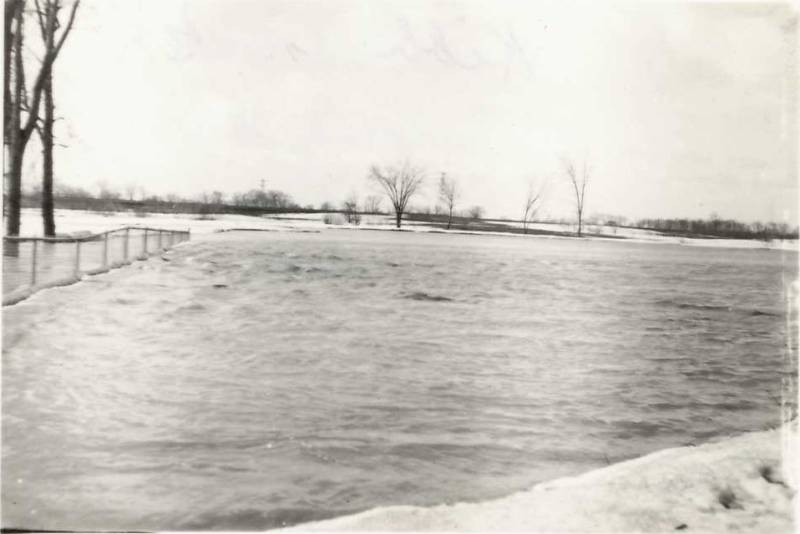
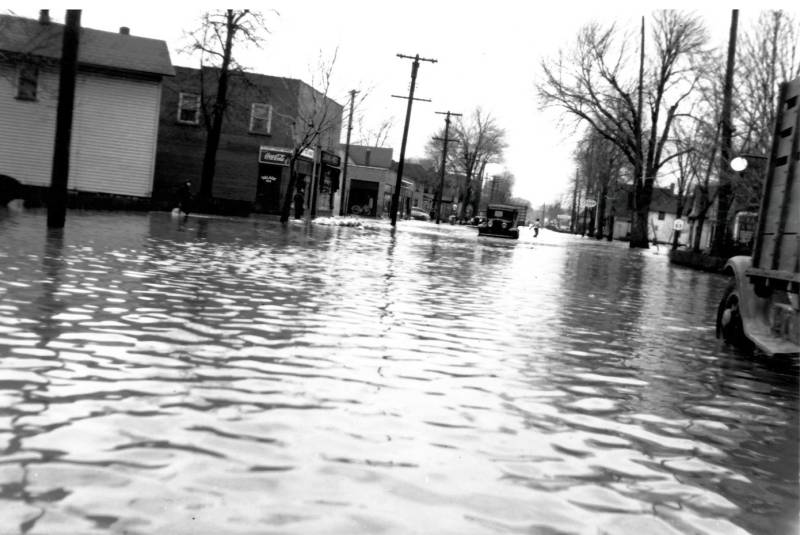
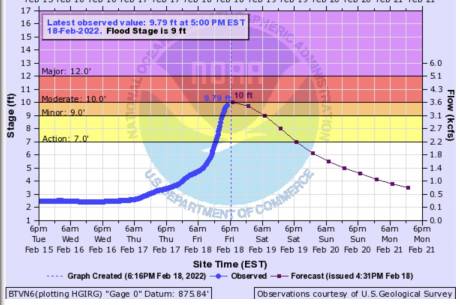
On Tuesday, for the fourth time in 2025, the Tonawanda Creek overflowed and flooded areas throughout the town of Alexander, including Peaviner Road.
This is an inconvenience to motorists, damages roads, takes farm fields out of production, and costs taxpayers money.
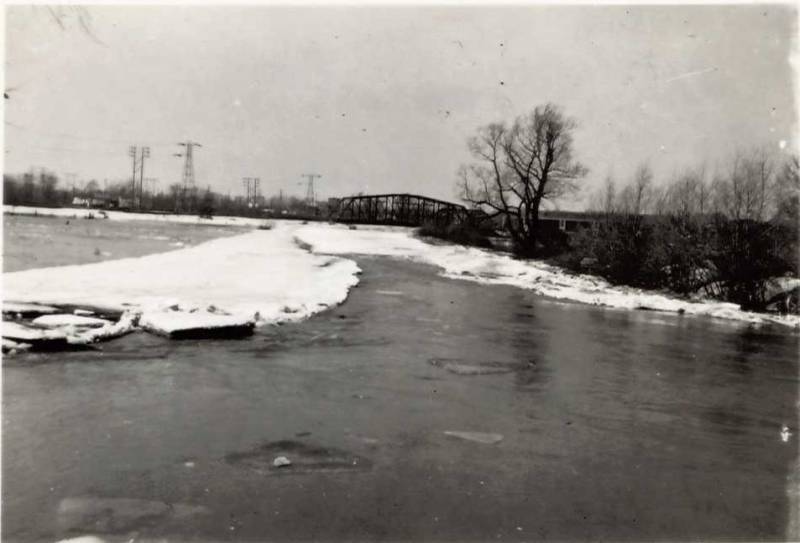
Brian Farnsworth, Alexander's highway superintendent, says the problem would be solved with an annual cleanup of the creek further upstream, where trees fall into the creek, creating a natural dam that eventually overflows, sending a rush of water north that causes flooding.
"If we could get in there somehow or another and clean all the trees that are down, I think it would open it up where this water would run," Farnsworth said. "We wouldn't have, like down here on Peaviner, water that runs off from the creek. We wouldn't have that. It would slow the overflow."
Farnsworth said he's hoping to secure grants for the creek cleanup. Clearly, the log jams probably need to occur on an annual basis, he said, because erosion keeps knocking big trees into the creek.
"It puts a burden on the taxpayers in Alexander because we have to keep going back to Old Creek Road and Cookson Road, and we have to keep going back and fixing the roads," Farnsworth said. "They're all dirt roads, but it just washes them out, and then we've got the material and the labor to take care of it, plus it's a major inconvenience, because a lot of people go down this road."
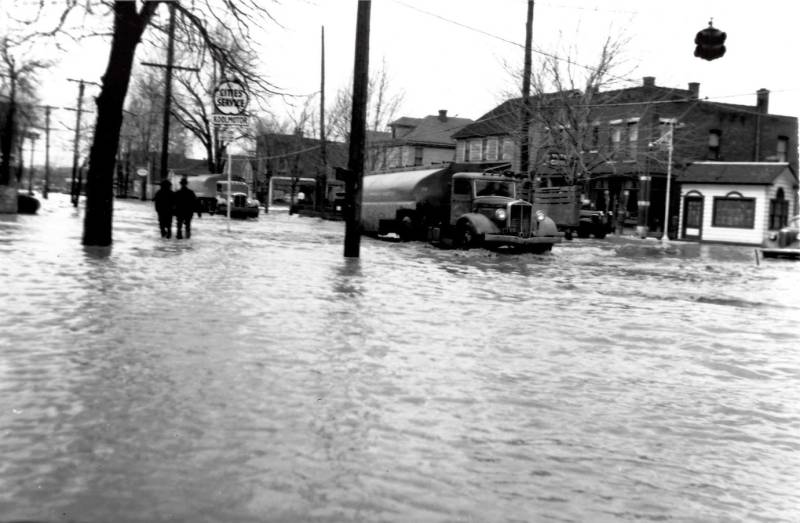
There is also a danger to motorists and first responders because some people do, in fact, try to drive through the floodwaters.
"If somebody comes down here and they do get stuck, it puts a burden on the sheriff's department and our first responders," Farnsworth said."They have to go in there and rescue them."
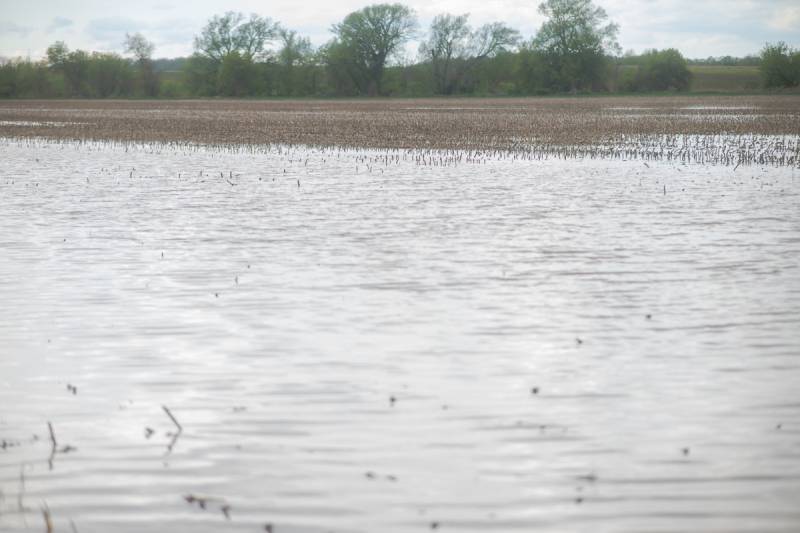
As for the farmers, he said, they get wiped out, he said.
"The various fields, they get wiped out. They can't plant. They can't do anything because of the water runoff."
Peaviner Road is now (on Wednesday) clear, and Cookson Road should clear by early afternoon.