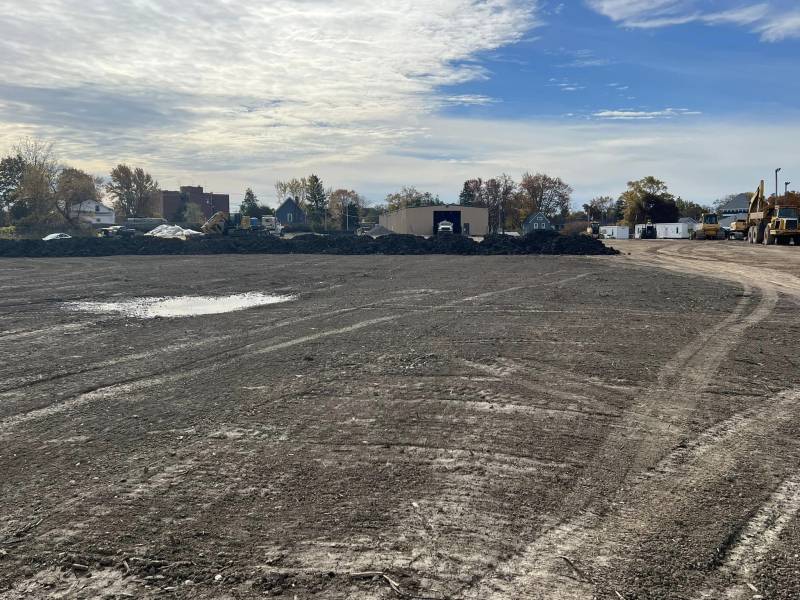
Ton by ton, city brownfield site gets restored for future use
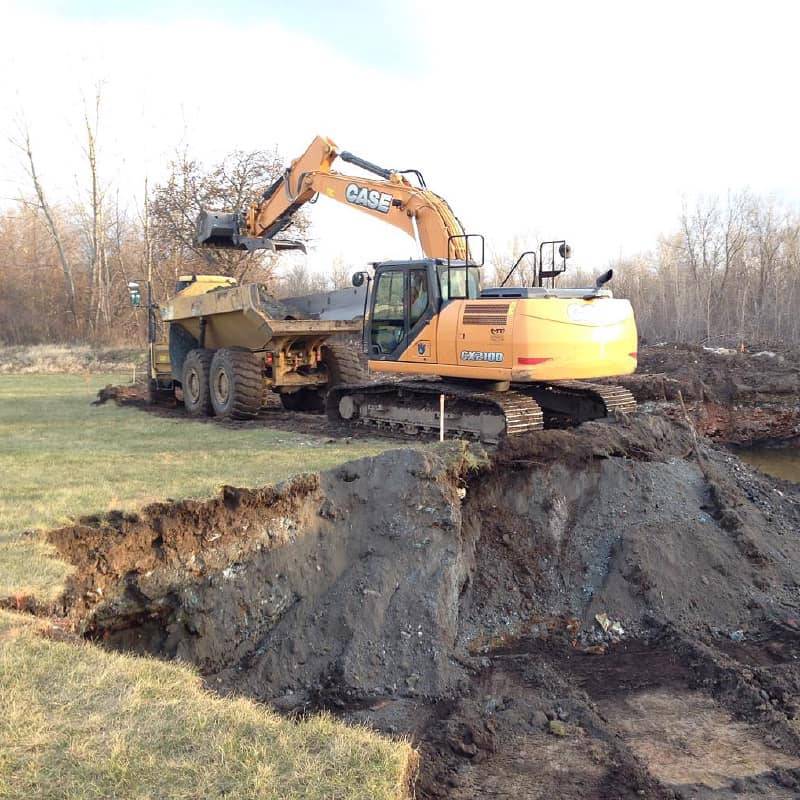

Photo from City of Batavia online post
City officials have been keeping a close eye on the Bank Street property once owned and operated by Batavia Iron and Metal Company, and in more recent months, where the grounds have been the target of remediation work by the state Department of Environmental Conservation.
Although the City of Batavia no longer owns the property and will likely move to foreclose on it and devise a re-use strategy, City Manager Rachael Tabelski said she is pleased with all that has taken place there since the DEC has claimed it as a Superfund site for brownfield cleanup.
“Re-use of the site will be dependent on the level of clean-up. If the site has been cleaned to unrestricted, residential and/or commercial activities would be allowed there,” Tabelski said. “The work the DEC has done at this parcel is truly amazing, and on behalf of the City, I would like to thank the members of the site cleanup team, from the engineers, construction, monitors, trucking, etc. and DEC for the leadership and prioritizing community health. Any time a brownfield site in our city is cleaned up, either by the DEC or a private developer, it is an accomplishment we should celebrate.”
The city threw that celebration online recently with some photos of the work-in-progress at the site that sits between Dwyer Stadium and private homeowners.
Photos from City of Batavia online post

Back then
After nearly 50 years operating as a metal recycling business and then sitting defunct for another dozen or so years next to Dwyer Stadium, Batavia Iron and Metal has been on a slow track for cleanup, and the next phase to get it back on the tax rolls began more than a year ago, Jeff Wernick of New York State Department of Environmental Conservation said previously.
DEC put out a call for bids to conduct remediation of approximately 50,000 tons of PCB-impacted soil for off-site disposal, backfill and restoration, Wernick said in response to The Batavian’s inquiries in 2022.
“DEC received four viable bids,” Wernick said. "The bids are associated with the remediation efforts under the State Superfund program. Work is being performed under a self-implementation agreement with the United States Environmental Protection Agency. DEC’s role for future use is limited to the completion of the cleanup activities and the release of the remediated site for residential or commercial use in accordance with local zoning ordinances.”
The winning bid award is expected in the fall, with work to start in the spring of 2023, he said. The scope of work is estimated to cost $15 million to $20 million. Remedial activities include the removal of PCB-contaminated soil, temporary water treatment, backfill, and restoration, including the transport and disposal of non-hazardous and hazardous soils.
The site at 301 Bank St., Batavia, earned special attention from the Department of Environmental Conservation more than a dozen years after it went defunct and was abandoned. Cleanups had been initiated for neighboring properties and the business site from 2013 to 2018.
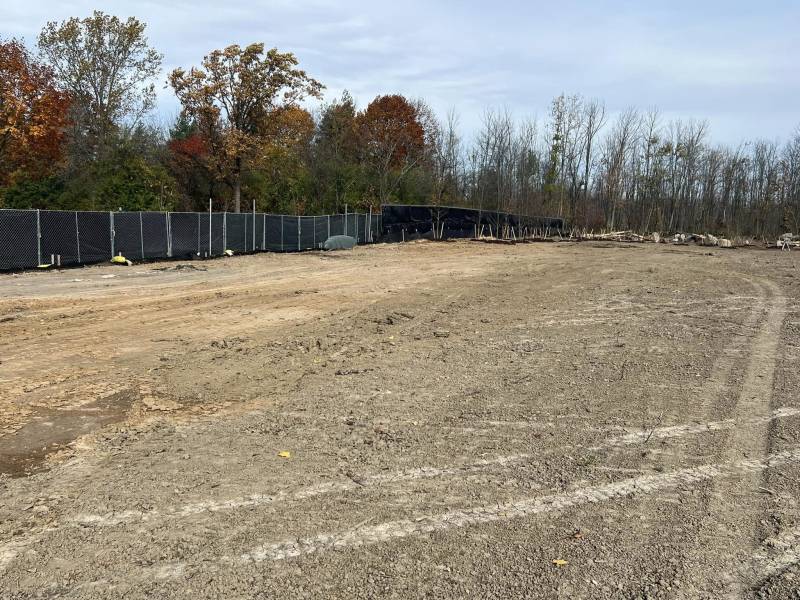
And now
Since then, DEC has been overseeing the comprehensive cleanup that, once complete, “will be fully protective of public health and the environment,” DEC Assistant Public Information Officer Denis Slattery said Friday. “Remedial work at the site is moving forward as scheduled with the transport and disposal of 65,000 tons of impacted soil and debris to off-site permitted facilities, as well as backfilling, and restoration of wetland areas.
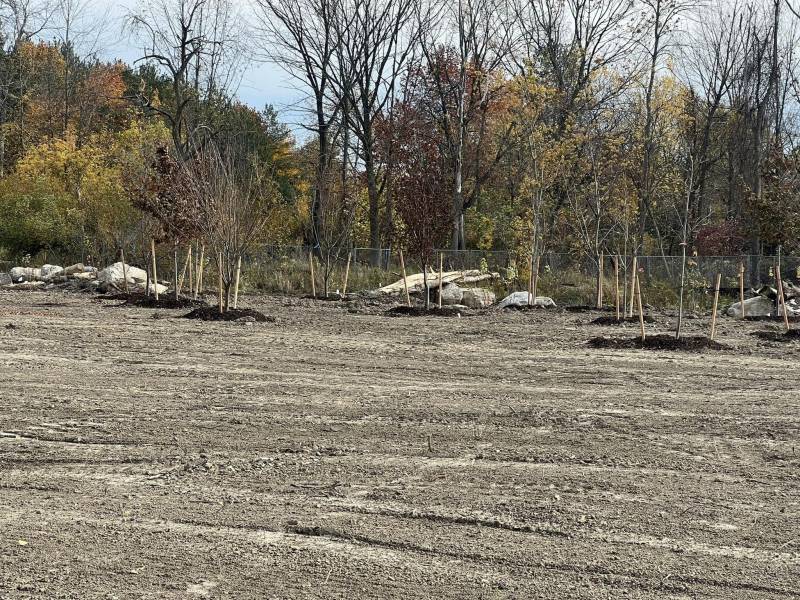

“Areas suitable for fall planting and seeding will be restored before work shuts down for the winter in December,” he said. “Site activity will resume in the spring with the restoration of paved areas and permanent fencing.”
Work is projected to be completed by summer 2024, he said. The site is anticipated to be restored for commercial use under an easement in accordance with local zoning laws.
“DEC will continue to coordinate with the city as the project moves toward completion,” Slattery said.
A DEC fact sheet from 2018 states that, based on the April 2013 Record of Decision, the cleanup included removal of contaminated soil and debris and from on-site and parcels located near the former facility. The Site operated as a metal recycling facility from 1951 to 1999.
Batavia Iron and Metal aftermath
Batavia Iron and Metal also purchased and handled electrical transformers on the property. Two furnaces operated at the facility from the early 1970s until 1994 for the purpose of reclaiming wire and smelting white metals. Prior to the use of the furnaces, the facility utilized open burning in Dumpsters in the yard to remove insulation from the wiring.
DEC took charge of designing and implementing this cleanup to remove the contaminants that have migrated from the site onto City property, the Fact Sheet states. As part of the remedy, the installation of sub-slab depressurization systems at three residences near the site was completed in 2013. In addition, a cleanup involving soil removal at three residences was completed in 2014.
Further work included soil removal and restoration activities along the rear property boundary of 299 Bank Street and 301 Bank Street. The goal of the cleanup effort was “to ensure the effective removal and proper disposal of contaminated soil and to restore the property with clean soil.” At least one neighbor — who lives next door to the defunct business — had complained about potential health issues from toxins leaching into his water system and how his trees would not grow in the contaminated soil.
Work done in 2017 was performed by Nature’s Way Environmental of Alden, with oversight and inspection provided by DEC. Soil identified for remediation was to be excavated and disposed of off-site. All areas that were disturbed during the removal were also to be restored, and the same for any City of Batavia-owned roads, utilities, or other infrastructure impacted by the cleanup activities.
DEC and the New York State Department of Health approved a Community Air Monitoring Plan that required continuous air monitoring during all excavation and backfilling activities to ensure no additional contamination was released to the environment or adjacent properties during the cleanup.
The project is being funded and conducted pursuant to terms of the State Superfund program, intended for “Brownfield” areas that are contaminated with toxic waste and in need of remediation for safe future use.